Can I Generate Code Using Generative AI Models? A Practical Guide

Let's cut right to the chase: yes, you can absolutely use generative AI to write code. In fact, it's quickly becoming a standard part of the modern developer's toolkit. Think of it less like a replacement for your skills and more like having an expert pair programmer on call 24/7, ready to handle the grunt work and offer instant solutions.
Yes You Can Generate Code With AI to Accelerate Development

This new partnership between human developers and AI is already making a huge impact on how software gets built. By automating tedious tasks like writing boilerplate code, generating unit tests, or even drafting entire functions, AI frees you up. You can spend less time on repetitive chores and more of your brainpower on the stuff that really matters—like tough architectural problems, creative solutions, and nailing the user experience.
The numbers back this up. Grand View Research expects the market for AI in coding to jump from USD 19.13 million in 2022 to a staggering USD 106.3 million by 2030. That growth is fueled by real-world results. For instance, developers using tools like GitHub Copilot have reported finishing their tasks up to 55% faster. It’s a massive productivity boost.
The Rise of the AI Co-Pilot
For most developers, the go-to method for using this tech is through an "AI co-pilot." These are tools that plug right into your favorite code editor, offering suggestions and completing code as you type. It’s like having a smart assistant who can instantly:
- Generate all the boilerplate code for a new class or file.
- Finish writing a function just from reading your comment or the function name.
- Suggest different ways to solve a tricky logical problem.
- Translate code snippets from one language to another, like Python to JavaScript.
This isn't about letting the AI take over. It's about shifting your role. You become the architect and the reviewer, guiding the AI to get the right results while you ensure everything is high-quality, secure, and works as intended.
The ability to generate code is just one piece of a much larger puzzle. To get a better sense of the entire field, this complete guide to AI engineering services offers a great overview of the foundational technologies involved. Knowing the bigger picture helps you understand how these powerful assistants are built and why they’ve become such a critical part of a modern development workflow.
To put it simply, AI code generation offers some immediate and powerful benefits that can change the way you work.
Key Benefits of AI Code Generation at a Glance
| Benefit | Description | Example Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Productivity | Automates repetitive and time-consuming coding tasks. | A developer finishes a feature in 3 hours instead of 5 by auto-generating unit tests and boilerplate. |
| Faster Learning | Provides instant examples and explanations for new languages or frameworks. | A junior developer learns React faster by seeing how the AI structures components and handles state. |
| Reduced Cognitive Load | Frees up mental energy to focus on high-level design and problem-solving. | Instead of remembering exact syntax, a programmer can focus on the core logic of an algorithm. |
| Improved Code Quality | Suggests best practices, identifies potential bugs, and ensures consistency. | The AI can suggest a more efficient way to query a database, preventing performance bottlenecks. |
Ultimately, these tools are designed to help you write better code, faster. They handle the tedious parts, letting you focus on the creative and complex challenges that make software development interesting.
How AI Actually Learns to Write Code
So, how does an AI model go from zero to writing functional code? It's not magic. Think of it more like an apprentice developer who has spent years studying millions of open-source projects. Generative AI learns to code through a kind of massive digital immersion, much like how we'd learn a new language by living in another country.
These models, specifically a type you’ve probably heard of called Large Language Models (LLMs), are trained on absolutely enormous datasets of code. Imagine feeding the entire public library of GitHub into a single brain—billions of lines of code written in Python, JavaScript, Java, you name it.
But the AI isn't just memorizing lines of code. Instead, it's absorbing the deep patterns, the syntax, and the logical structures that make software work. It learns what a typical for loop looks like in Python, how to build a standard API request in JavaScript, and the right way to structure a class in C++.
From Generalist to Specialist
Not all code-generating AI models are the same. Some are generalists, while others are specialists fine-tuned for programming. Understanding this difference is key to knowing what to expect from them.
- General-Purpose LLMs: These are the jacks-of-all-trades, trained on a huge mix of text and code. They can write a Python script, but they can also draft an email or answer a history question. Their coding skills come from the code that happened to be in their massive, diverse training data.
- Code-Specific Models: These are the experts. Models like OpenAI's Codex, which is the engine behind GitHub Copilot, have been fine-tuned specifically on code. After their initial broad training, they go through a second, more intense phase focused only on programming languages and development patterns.
This fine-tuning process is like sending a liberal arts grad to a specialized coding bootcamp. They already have a solid foundation in language, but now they're diving deep into the nuances of programming. The result? Their code output is far more accurate, idiomatic, and reliable.
At its heart, this is all about pattern recognition and prediction. The AI doesn't "understand" code in the way a human developer does. It's making a highly educated guess about the most probable next piece of code based on the millions of examples it has already seen.
Why High-Quality Data is Everything
The old saying "garbage in, garbage out" has never been more true. An AI's output is a direct reflection of the data it was trained on.
If a model learns from clean, well-documented, and efficient code, it’s much more likely to generate code with those same positive traits. On the flip side, if its training data is full of bugs, security holes, or outdated practices, the AI will happily reproduce those same flaws in its own suggestions.
This is why data curation is such a critical step. The companies building these models spend a ton of resources cleaning and filtering their datasets, making sure the AI learns from the best examples out there. At the end of the day, an AI's ability to write good code all comes down to this foundational process: learning from our collective work to predict what should come next.
Picking the Right AI Coding Assistant for the Job
Not all AI coding assistants are built the same. Just like a mechanic has a whole toolbox—a wrench for one job, a diagnostic scanner for another—developers have different kinds of AI assistants for different tasks. Figuring out these categories is the first step to choosing a tool that will actually fit into your workflow and help you write better code.
The market for these tools is exploding. It kicked off at USD 18.34 million in 2023 and is on track to hit USD 139.55 million by 2032. A huge part of that growth comes from code generation and autocompletion tools, which made up 44% of the market's revenue in 2023 by offering those handy real-time suggestions that save time and prevent silly mistakes.
With a staggering 41% of all code now being generated by AI, it’s safe to say these assistants are becoming a standard part of a developer's kit.
What Are My Options?
To make sense of it all, let's break down the main types of AI coding tools you'll encounter. Each has its own strengths and is designed for a specific kind of work.
The table below gives you a quick snapshot of the different categories, what they're best for, and some popular examples you might have heard of.
Comparison of AI Coding Assistant Types
| Tool Type | Primary Use Case | Strengths | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Code Completion | Real-time, in-editor suggestions | Speeding up boilerplate code, reducing typos, completing lines and functions | GitHub Copilot, Tabnine, Amazon CodeWhisperer |
| Conversational AI | Chat-based problem-solving | Generating full scripts, explaining code, debugging complex issues, brainstorming | ChatGPT, Google Gemini, Claude |
| Code Generation Platforms | Building entire applications from prompts | Rapid prototyping, creating full-stack apps, automating large-scale code creation | v0.dev, Cursor, Replit AI |
As you can see, the right choice really depends on what you're trying to accomplish at that moment.
Code Completion Tools: Your In-Editor Sidekick
The most familiar type of AI assistant is the one that lives right inside your code editor, whether that's VS Code or a JetBrains IDE. Think of these as autocompletion on steroids.
They work by constantly analyzing the context of your current file—your comments, function names, and the code you’ve already written—to predict what you’re trying to do next.
They’re brilliant for speeding up the line-by-line grind of coding. They finish your sentences, fill in repetitive boilerplate, and catch minor syntax mistakes before they happen.
For example, you might type def calculate_average(numbers): and GitHub Copilot will instantly suggest the entire function body—summing the numbers, dividing by the count, and all.
This workflow is all about taking data, training on it, and then using those patterns to produce useful code right where you need it.
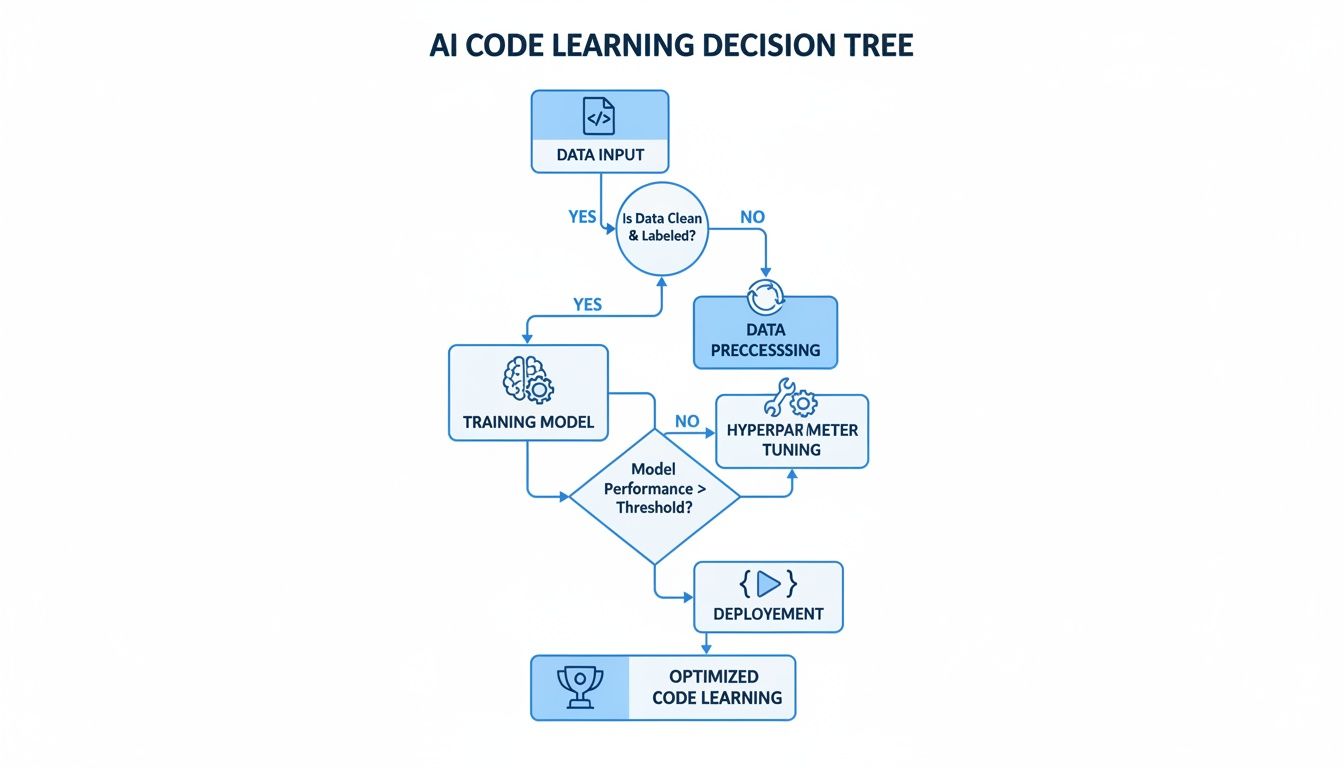
This process really shows how an AI's output is a direct reflection of the quality and patterns it learned from its training data.
Conversational AI: Your Brainstorming Partner
Unlike tools that live in your editor, conversational AI models like ChatGPT or Google's Gemini feel more like a collaborator you can talk to. You use a chat window to give them detailed instructions, and they give you back complete blocks of code.
Here’s the key difference: While code completion tools are for the tactical, moment-to-moment flow of writing code, conversational AI is for more strategic, big-picture problem-solving. You use it to hash out ideas, debug a tricky issue, or generate an entire component from scratch.
You could ask it something like, "Write a Python script with pandas to read a CSV, drop duplicate rows based on the 'email' column, and save the clean data to a new file." The model spits out a complete script that you can copy, review, and drop into your project.
To get a better handle on how these models actually work, our guide on using an LLM for code generation goes into much more detail.
Ultimately, choosing the right tool comes down to your immediate goal. Trying to code faster, line by line? A code completion tool is your best friend. Stuck on a complex problem and need a full solution you can adapt? A conversational AI is the perfect place to start.
How to Write Prompts That Generate Great Code
The quality of the code an AI gives you hinges almost entirely on one thing: the quality of your prompt.
Asking an AI to "write a function" is a bit like asking a chef to "make food." Sure, you'll get something, but it's a gamble whether it's what you actually wanted. To get great code, you need to hand the AI a detailed recipe.
This means you have to move past simple requests. You need to give the model specific, contextual, and well-structured instructions. Think of it less like a conversation and more like writing a clear spec sheet. The more detail you provide, the less the AI has to guess, and the closer the output will be to something you can actually use. Vague prompts just lead to generic, often buggy, results.
The Anatomy of an Effective Code Prompt
A powerful prompt is a blueprint. It’s not just one sentence; it's a collection of key details that guide the model straight to the code you need.
A well-structured prompt should always include:
- Language and Framework: Right at the start, state the programming language (Python, JavaScript, etc.) and any libraries or frameworks involved (like React, pandas, or Express.js).
- The Function's Purpose: In simple terms, what should this function do? What's its goal?
- Inputs and Outputs: Get specific. Define the function signature, including what parameters it takes, their data types, and what it should return.
- The Core Logic: Briefly explain how it should work. Does it need to loop through a list? Make an API call? Perform a specific calculation?
- Error Handling: Don't forget this! Tell the model how to handle things when they go wrong. Should it throw an exception or return
nullif an input is bad?
Here’s a great example of a detailed prompt designed to generate a Python function.

This screenshot shows exactly how breaking down your instructions into clear, logical chunks helps the AI deliver predictable and accurate code.
Bad Prompt vs. Good Prompt: A Practical Example
Let's look at the difference this makes in a real-world scenario. Say you need a function to fetch user data from an API.
Bad Prompt: "Write a JavaScript function to get user data."
This is far too vague. The AI is left to guess the API endpoint, the error handling logic, and the data structure. You'll probably get a generic snippet that you have to completely rewrite.
Now, let's try again with a more structured approach.
Good Prompt:
"Write an asynchronous JavaScript function namedfetchUserDatathat accepts auserIdas a number.
Functionality:It should use thefetchAPI to make a GET request tohttps://api.example.com/users/{userId}.If the request is successful (status 200), it should return the JSON response.If the user is not found (status 404), it should returnnull.For any other network or server errors, it should throw an error with the message 'Failed to fetch user data'."
See the difference? This prompt leaves nothing to chance. The AI knows the exact language, function name, parameters, endpoint, and the logic for both success and failure. Learning to write prompts like this is a real skill. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on the best AI prompts for programming to see even more advanced patterns.
Getting good at this is non-negotiable if you want to generate useful code with AI. The next challenge, especially for teams, is keeping all these detailed prompts organized. That's where a tool like Promptaa comes in. It gives you a place to create, save, and share a library of tested, high-quality prompts so your whole team can get consistent results every single time.
Navigating the Risks and Best Practices of AI Code
Using AI to generate code can seriously speed up your workflow, but it’s not a magic bullet. Tapping into these tools means taking on some new responsibilities. The best way to think of an AI model is like a brilliant but incredibly fast junior developer—it produces work that looks solid at first glance but absolutely needs a senior developer's eye before it gets anywhere near production.
This oversight is non-negotiable. AI models can introduce subtle yet serious risks. They might spit out code with hidden security flaws, pull in outdated libraries, or even copy-paste snippets from their training data that are tied to restrictive software licenses. At the end of the day, you're the one on the hook for every single line of code that gets committed, no matter where it came from.
Adopt a "Trust but Verify" Mindset
The secret to using AI for code generation safely is to operate with a strict "trust but verify" policy. The numbers don't lie: developers are jumping on this trend fast. By the first quarter of 2025, an estimated 82% of developers are expected to use AI tools every week, with 59% using three or more.
But that speed comes with a price. One analysis of 153 million lines of code found that code duplication has shot up fourfold, a clear sign of how quickly AI-generated patterns can spread if left unchecked.
To get a handle on this and make sure you're deploying AI-assisted code responsibly, a good AI production readiness checklist can be a lifesaver. It gives you a clear framework for validating what the AI gives you before it goes live.
Your Checklist for Safe AI Code Generation
Let's make this practical. Here’s a simple checklist you can weave into your daily workflow. Following these steps helps you get the speed benefits of AI without trashing the quality and security of your codebase.
- Always Review and Refactor: Treat every piece of AI-generated code like a first draft. Always. Go over it for logic, efficiency, and to make sure it matches your team's style guide. Then, refactor it until it fits seamlessly into your existing architecture.
- Integrate Security Scanning: This one is huge. Plug automated security scanners directly into your CI/CD pipeline. Tools like SAST (Static Application Security Testing) are great at catching common vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting that an AI might accidentally bake into the code.
- Validate for Hallucinations: AI models are known to "hallucinate," which means they can literally invent functions, libraries, or API endpoints that don't exist. You have to run and test the code to make sure every single piece of it is real and works correctly. Our guide on how to reduce hallucinations in LLMs has more tips for managing this.
- Check for License Compliance: Use a tool to scan for license violations. Since these models train on mountains of public code, they can sometimes reproduce snippets that require attribution or are covered by a license that's incompatible with your project.
By treating the AI as a powerful but flawed partner, you can bring it into your development process safely. This balanced approach lets you take advantage of its incredible speed while holding onto the high standards of quality, security, and reliability that professional software demands.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Code Generation
As developers start messing around with AI for coding, a lot of practical questions pop up. Moving from writing every single line by hand to working alongside an AI is a big shift, and it naturally brings up questions about job security, what these tools can actually do, and how to use them safely.
This section tackles the most common questions we hear from developers who are just getting started with generating code using AI.
Will Generative AI Replace Software Developers?
It’s extremely unlikely. Think of it more like AI will supercharge developers, not replace them. This is a lot like how power tools didn't get rid of carpenters—they just made them way more productive. AI assistants are brilliant at taking care of the tedious, repetitive, and boilerplate code that drains a developer's time.
By automating the boring stuff, developers get to focus their brainpower on the work that really matters:
- High-level system architecture and creative design.
- Solving complex problems that demand real ingenuity and context.
- Guiding, reviewing, and weaving together AI-generated code to make sure it’s high-quality and secure.
The job is definitely changing. The most successful developers will be the ones who learn to master these tools, becoming expert "AI collaborators" who build better software, faster.
What Programming Languages Can AI Generate?
Today’s generative AI models are incredibly flexible and can handle a huge range of programming languages. They’ve learned from massive public codebases like GitHub, so they're sharpest with languages that have a ton of examples out in the wild.
You’ll find excellent support for all the big ones:
- Python
- JavaScript & TypeScript
- Java & C#
- C++
- Go
- SQL
But it doesn't stop there. These models can also whip up code for less common languages, shell scripts, and even markup like HTML and CSS. Just remember, the quality of the code it spits out is directly related to how much training data it had for that specific language and its popular frameworks.
How Do I Integrate AI Into My Workflow?
Getting started is actually pretty simple. Most of these tools are built to slide right into the environments developers already use every day. The most popular way is by installing an extension in your favorite Integrated Development Environment (IDE).
You can find AI coding assistants for just about everything: VS Code, the entire JetBrains suite (like IntelliJ IDEA or PyCharm), and Visual Studio. Once you install a tool like GitHub Copilot, it starts offering suggestions and completions in real-time as you type, making it feel like a natural part of your process.
For bigger tasks, like generating a whole function or debugging a thorny issue, you can chat with an AI in a separate window. Once you've checked its work, you just copy and paste the code into your project. A great way to ease into it is by using AI for autocompletion and generating unit tests, then slowly letting it handle more complex jobs as you get comfortable.
Is AI Generated Code Secure and Original?
This is a huge one, so let’s be clear: AI-generated code is not guaranteed to be secure or original. At the end of the day, you are responsible for every line of code you commit. Since these models learn from public code, they can accidentally copy insecure patterns or generate snippets that are almost identical to code from their training data.
This introduces two major risks:
- Security Vulnerabilities: The AI might suggest code with classic flaws like SQL injection vulnerabilities or poor error handling.
- License Infringement: It could produce code that comes from a project with a restrictive license, which might not be compatible with your own.
Here’s the golden rule: treat all AI-generated code like it was written by a new junior developer on your team. You have to review it carefully, test it for bugs and security holes, and use scanning tools to make sure you’re not violating any licenses. Human oversight isn’t just a good idea—it’s absolutely essential for building a professional and secure codebase.
Ready to create better, more consistent prompts for code generation? Promptaa gives you the tools to build and share a powerful library of AI-enhanced prompts, ensuring you and your team get the high-quality results you need every time. Start organizing your prompts today at https://promptaa.com.