A Guide to AI Prompts Engineering
Prompt engineering is less about coding and more about clear communication. Think of it like being a director for a very talented, very literal actor. The better your instructions, the more compelling the performance. It's the skill that transforms a fascinating but sometimes unpredictable AI into a reliable creative partner.
Understanding the New Language of AI
At its heart, AI prompt engineering is the craft of designing specific inputs—or prompts—to get exactly what you want from large language models (LLMs) like OpenAI's GPT-4. It goes way beyond just asking a simple question. It's about giving the AI the right context, setting clear boundaries, and even providing examples to shape its output with incredible precision.
The quality of what you get out of an AI is a direct reflection of the quality of what you put in.
It's a lot like briefing a new team member. A vague request like "write something about business" will get you a generic, probably useless, response. But a detailed instruction like, "Write a 500-word blog post in a confident, authoritative tone about the top three challenges for small business owners in 2024," sets the stage for a great result. That’s the real difference between just using AI and engineering a prompt. For a deeper dive, check out our complete guide on what prompt engineering is and how to unlock AI's full potential.
Why Prompt Engineering Matters Now
Knowing how to "talk" to an AI is quickly moving from a niche tech skill to a basic form of digital literacy. From marketing and content creation to software development and customer service, businesses are weaving AI into everything they do. This has created a huge demand for people who know how to get the most out of these powerful tools.
This isn't just a fleeting trend; it's a massive economic shift.
The global market for prompt engineering is exploding right alongside generative AI. Valued at roughly USD 380.12 billion in 2024, it's expected to soar to an incredible USD 6.53 trillion by 2034.
This stunning growth sends a clear message: mastering AI communication gives you a serious competitive edge, whether you're an individual professional or an entire organization. You can learn more about the rapid expansion of this market.
The Building Blocks of a Great Prompt
So, what separates a simple question from a professionally engineered prompt? It all comes down to a few key ingredients that remove ambiguity and guide the AI toward the perfect response.
Here's a quick look at the core components that make up a well-crafted prompt. Think of these as the fundamental building blocks for getting consistent, high-quality results from any AI model.
Core Components of an Effective AI Prompt
By weaving these elements together, you stop just asking the AI for things and start collaborating with it to create exactly what you need. This level of control is what makes AI prompt engineering such an empowering and valuable skill today.
Core Principles for Effective Prompting
Getting great results from an AI isn't about finding some "magic word" that unlocks its full potential. It's really about building your requests on a few solid principles. These are the fundamental rules of the road for ai prompts engineering, and they're what separate a hopeful guess from a reliable instruction.
Think of it like this: you can either give someone vague directions or hand them a detailed map. One leads to you getting lost, while the other gets you exactly where you want to go. Nailing these fundamentals is the first real step toward getting predictable, high-quality results from any AI model.
Be Explicitly Clear and Unambiguous
The single biggest mistake people make when writing prompts is assuming the AI knows what they mean. Large language models are incredibly smart, but they can't read your mind. Vague language is the enemy of a good prompt because it forces the AI to guess, and those guesses often lead to generic or totally off-the-mark answers.
Your main job is to remove every ounce of ambiguity. Make your instructions direct and leave zero room for misinterpretation.
Let's look at a classic vague request: Write about business.
Where does the AI even start? It could write about corporate finance, famous entrepreneurs, or the basics of starting a company. The result is a complete roll of the dice.
Now, let's inject some much-needed clarity: Write a 500-word blog post in a confident, authoritative tone about the top three challenges for small business owners in the e-commerce sector.
See the difference? This version is specific and actionable. It defines the format (blog post), word count (500), tone (confident, authoritative), topic (top three challenges), and the specific audience (e-commerce small business owners).
Key Takeaway: The more precise your language, the more precise the AI's output. Treat every prompt like you're writing a formal set of instructions for a very literal, very powerful assistant.
Provide Rich and Relevant Context
Context is all the background information that gives your prompt meaning and direction. Without it, the AI is working in a vacuum, trying to figure out what you want from just a few clues. It’s the difference between giving a historian a single headline versus giving them the full story behind an event.
For instance, asking an AI to Write a marketing email is a total shot in the dark. It has no idea what you’re selling, who you’re talking to, or what you want the email to achieve.
A much better approach is to provide the essential context right up front:
- Product: A new line of eco-friendly, reusable coffee cups.
- Target Audience: Environmentally conscious millennials aged 25-35.
- Goal: Drive pre-orders with a limited-time 20% discount.
- Key Selling Points: Made from recycled materials, dishwasher-safe, and has a stylish, minimalist design.
When you frame your request with this kind of information, you're giving the AI the raw materials it needs to build a message that actually works. This is a cornerstone of effective ai prompts engineering. If you want to dive deeper, this guide to mastering prompt optimization as the key to unlocking AI’s full potential is a great next step.
Use Constraints and Define the Format
Just as important as telling the AI what to do is telling it what not to do—and how you want the final output structured. Constraints act like guardrails, keeping the AI focused on the task at hand and preventing it from wandering off-topic or giving you a response in a totally useless format.
Setting these boundaries is a powerful way to fine-tune the AI’s output.
Here are a few common constraints you can use to get better results:
- Impose a Persona: "Act as a seasoned travel blogger who has visited Italy ten times." This immediately sets a specific voice, tone, and level of expertise.
- Define the Structure: "Present the information as a numbered list," or "Create a table with three columns: Feature, Benefit, and Example."
- Specify Exclusions: "Do not mention any of our competitors by name," or "Write this for a non-technical audience, so avoid using industry jargon."
By setting these rules, you guide the AI to deliver content that not only meets your needs but is also perfectly formatted for its final destination. That alone can save you a ton of editing time.
Essential Prompt Engineering Techniques
Once you've got the hang of providing clear instructions and good context, you can start digging into the real craft of prompt engineering. This is where you move beyond just talking to an AI and start strategically guiding it.
Think of these techniques as different tools in a toolbox. You wouldn't use a sledgehammer to hang a picture frame, right? The same logic applies here. Knowing which technique to pull out for a specific job is what separates a novice from an expert, giving you precise control over the AI's output.
Building Blocks: The “Shot” Methods
One of the most powerful and intuitive ways to get better results is to simply show the AI what you want. This is the whole idea behind "shot-based" prompting, where a "shot" is just a fancy word for an example you include in your prompt.
- Zero-Shot Prompting: This is the most basic approach. You give the AI a task with zero examples and rely on its existing knowledge. It works fine for simple, common requests but struggles when you need something specific or nuanced.
- One-Shot Prompting: Here, you provide a single, solid example of what you're looking for. Just one good model of an input and its corresponding output can give the AI a clear pattern to follow, which really boosts accuracy for specific formats.
- Few-Shot Prompting: When things get more complex, providing two to five examples is the sweet spot. This technique gives the model enough data points to reliably figure out the pattern, making it a go-to for tasks like sentiment analysis or sorting data into custom categories.
This image perfectly illustrates the difference. Moving from a vague, zero-shot prompt to one packed with examples makes a night-and-day difference in performance.
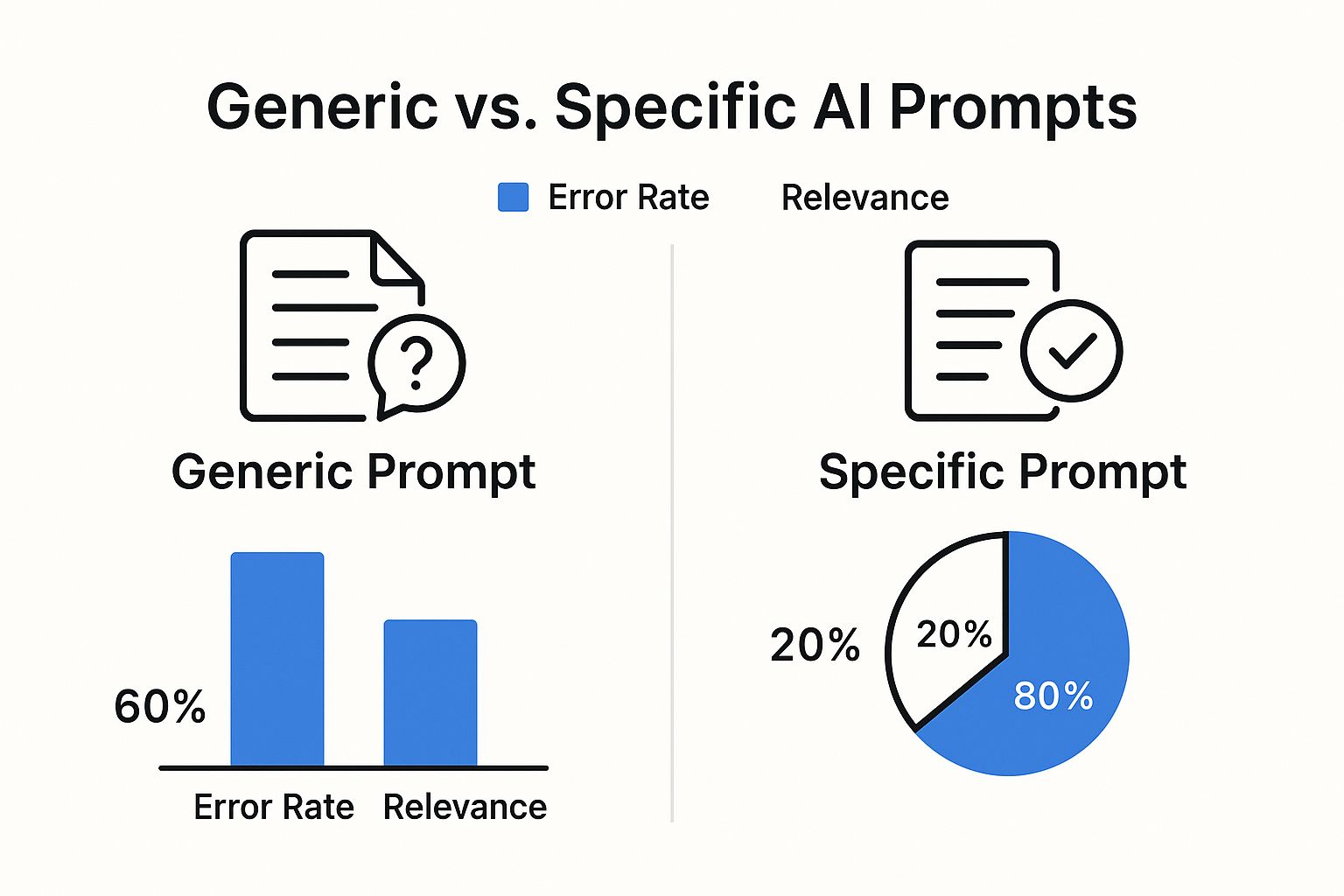
The takeaway is crystal clear: if you’re serious about getting high-quality results, providing examples is one of the fastest ways to slash errors and get the AI to generate exactly what you need.
Shot-Based Prompting in Action
Let’s make this concrete. Imagine you need to pull company names from blocks of text.
With a Zero-Shot prompt, you might write: Extract the company name from this sentence: "We are excited to announce a new partnership with Acme Corporation." An AI will probably nail that one.
But what happens when the text is less direct? That’s where Few-Shot Prompting shines. You teach it the pattern first.
Prompt:
Text: "I just bought a new phone from Apple." Company: Apple
Text: "The team uses Microsoft products daily." Company: Microsoft
Text: "Our next meeting is with the team from Stellar Solutions." Company:
By feeding it a few examples, you've trained the AI on the spot. It now understands the task's context and correctly identifies "Stellar Solutions" without any guesswork. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on how to write AI prompts that actually work.
Advanced Strategy: Chain-of-Thought Prompting
For problems that require actual reasoning, a simple instruction isn't enough. The AI will often rush to an answer and get it wrong. This is where Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting comes in.
Instead of just asking for the final answer, you instruct the AI to "think step-by-step" and lay out its logic.
This simple trick forces the model to break down a problem into smaller, manageable chunks. The result? A massive improvement in its ability to handle math, logic puzzles, and common-sense reasoning.
Let's say you give it a word problem: If a cafe has 25 tables, and 15 are for two people and the rest are for four people, how many customers can it seat in total?
A standard prompt might spit out a number, possibly the wrong one. With a CoT prompt, you guide its thinking process.
CoT Prompt Example:
A cafe has 25 tables. 15 tables are for two people. The rest are for four people. Calculate the total number of customers the cafe can seat. Let's think step by step.
That last little phrase, "Let's think step by step," is the key. It prompts the AI to show its work first:
- First, find the number of four-person tables: 25 total tables - 15 two-person tables = 10 four-person tables.
- Next, calculate the capacity for two-person tables: 15 tables * 2 people/table = 30 people.
- Then, calculate the capacity for four-person tables: 10 tables * 4 people/table = 40 people.
- Finally, add them together: 30 + 40 = 70 total customers.
The AI's reasoning is now transparent, and the final answer is far more trustworthy. This kind of reliability is exactly why businesses are investing so heavily in these skills.
Comparing Prompting Techniques and Their Use Cases
Choosing the right technique can feel overwhelming, so here’s a quick-reference table to help you match the method to the mission.
This table should serve as a good starting point. As you get more experience, you'll develop an intuition for which approach will deliver the best results for your specific needs.
How Prompt Engineering Drives Real-World Results

It’s one thing to talk about the principles of prompt engineering, but seeing it in action is where things get really interesting. This isn't just some academic exercise; it's a skill that directly drives efficiency, sparks creativity, and boosts profits in countless industries. When you move from tossing simple questions at an AI to crafting well-engineered prompts, you unlock a serious competitive edge.
The difference is like a blurry sketch versus a high-resolution photograph. One gives you a vague idea, while the other delivers a clear, actionable picture. It's that clarity that leads to real business outcomes, turning AI from a cool novelty into a core part of how you operate.
From Marketing Copy to Code Generation
Take marketing, for example. Teams are now using detailed, persona-based prompts to create hyper-targeted ad copy that truly connects with specific audiences. Instead of asking for "ad copy for a new tool," a savvy marketer will build a prompt that details the target demographic, their biggest frustrations, and the exact emotional response they want to evoke. The result? Copy that actually converts.
Here's a quick look at what that might involve:
- Persona: Act as a marketing strategist for a SaaS company whose customers are swamped project managers.
- Context: Our product is a new task management tool that uses AI to automate deadline reminders and resource allocation.
- Task: Write three distinct Facebook ad headlines that highlight how our tool saves users at least five hours per week.
- Tone: Confident but empathetic. Focus on the benefits, not just the features.
This level of detail ensures the AI's output isn't just good writing—it's strategically sound. Over in the software development world, structured prompts are speeding up workflows at an incredible pace.
Developers are using prompt engineering to generate boilerplate code, debug tricky functions, or even translate code from one language to another. A well-crafted prompt that specifies the right libraries, frameworks, and coding standards can spit out clean, functional code in seconds. This frees up developers to focus on the big-picture problems that actually require human ingenuity.
The Financial and Operational Impact
The contrast between a disciplined prompting strategy and an "anything goes" approach has a measurable financial impact. It turns out that poor human-AI communication is a factor in roughly 78% of AI project failures. On the flip side, teams that implement skilled prompt engineering practices report a return on investment that's about 340% higher than those who don't.
These numbers aren't just trivia; they show how mastering this communication skill is critical for success. You can dig deeper into the vital role of prompt engineering in AI projects on cmswire.com.
This data proves that effective prompt engineering is not just a "nice-to-have" skill. It is a fundamental business competency that directly influences project success and financial returns in the modern economy.
Applications in Specialized Fields
The power of precise prompting goes far beyond just marketing and tech. In highly specialized fields like healthcare, it’s making a real difference in how information is managed and how patients are cared for.
Medical professionals can use sophisticated prompts to summarize complex patient histories, transcribe a doctor's spoken notes, or even explain dense medical research in plain language for patients to understand. A prompt engineered to recognize and prioritize key medical terms, symptoms, and treatments ensures that AI-generated summaries are both accurate and clinically useful.
Here’s a practical example of how it works:
- Input: A doctor uploads a long, unstructured transcript from a patient visit.
- Prompt: The AI is instructed to "Extract the patient's primary symptoms, list all prescribed medications with dosages, and summarize the recommended follow-up plan in a bulleted list for a medical assistant."
- Output: The AI instantly generates a clean, organized, and accurate summary, slashing administrative work and reducing the risk of human error.
From sparking a creative marketing campaign to writing clean code and summarizing critical medical data, prompt engineering is the essential skill that turns AI's potential into real-world performance. It’s the practical art of communication that allows us to direct these powerful tools to solve problems with precision and reliability.
Common Prompting Mistakes to Avoid
Getting good at ai prompts engineering is just as much about spotting what's wrong as it is about knowing what's right. Even the smartest AI will give you disappointing results if you feed it flawed instructions. The good news is that most of the common problems come down to simple communication errors that are surprisingly easy to fix.
Once you start recognizing these classic blunders, you’ll find yourself troubleshooting your own prompts in seconds. Let's break down the most frequent mistakes I see, so you can learn how to turn a weak prompt into a powerful one that gets you exactly what you need.
The Ambiguity Trap
The number one mistake people make is being too vague. AI can’t read your mind, so when your instructions are fuzzy, it has no choice but to guess. Ambiguity is the enemy of a good output, leading to generic, off-topic, or just plain wrong responses.
Let's say you're trying to come up with some product names.
- Bad Prompt:
Give me some names for a new shoe.
This prompt is a total guessing game for the AI. What kind of shoe? Who is it for? What's the brand all about? You'll probably get back a list of bland, uninspired names like "FitStep," "SoleMate," or "UrbanWalk."
The fix is to remove the guesswork by adding specific, defining details.
- Good Prompt:
Generate 10 product names for a new waterproof hiking boot for serious female mountaineers. The brand is rugged and adventurous. The names should evoke a sense of durability and exploration.
Now that's a prompt. It clearly states the product type (waterproof hiking boot), the audience (serious female mountaineers), the brand personality (rugged and adventurous), and the feeling the names should create (durability and exploration). The AI has a clear target to aim for, resulting in much stronger and more relevant ideas.
Forgetting to Provide Context
Context is all the background information that gives your request meaning. Without it, the AI is working in a vacuum. It might understand what you're asking, but it has no idea why. Giving context is like handing a painter a full photograph of a scene instead of just pointing at a single object.
A prompt without context is like an instruction without a goal. The AI might complete the task technically, but it will miss the strategic intent behind it.
Think about a common task like summarizing an article. The kind of summary you need depends entirely on the situation.
- Bad Prompt:
Summarize this article.
This request is far too simple. The AI doesn't know who the summary is for or what its purpose is. Should it be written for a CEO, a fellow engineer, or a potential customer?
- Good Prompt:
Summarize this attached technical article about quantum computing. The summary should be written for a non-technical marketing team. Focus on the real-world applications and potential business impact, and keep it under 200 words.
This version provides the critical context. It spells out the audience (non-technical marketing team), what to focus on (applications and impact), and a specific constraint (under 200 words). This ensures the summary isn't just accurate but is perfectly tailored for its real-world purpose.
Giving Conflicting Instructions
Another classic mistake is accidentally giving the AI contradictory commands in the same prompt. This usually happens when you ask for one thing but describe it in a way that implies something completely different. The AI gets stuck, not knowing which instruction to follow.
A common example is mismatching the tone and the topic.
- Bad Prompt:
Write a fun, upbeat, and exciting blog post about the serious financial risks of ignoring retirement planning.
The instructions are fighting each other here. The subject—"serious financial risks"—is inherently heavy, which clashes directly with the requested "fun, upbeat, and exciting" tone. The AI will struggle to make this work, and you'll likely end up with something that feels awkward or tonally bizarre.
The solution is to make sure every part of your prompt is aligned and pushing in the same direction.
- Good Prompt:
Write a clear, authoritative, and urgent blog post about the serious financial risks of ignoring retirement planning. Use strong, direct language to motivate young professionals to take action.
By aligning the tone (authoritative, urgent) with the serious topic, you give the AI a clear, consistent mission. This is a core part of effective ai prompts engineering—making sure all your instructions work together in harmony.
The Future of Human and AI Collaboration

As we look to the future, AI prompt engineering is quickly shedding its reputation as a niche technical skill. It's becoming a new kind of digital literacy, essential for almost everyone. The conversation is no longer just about giving an AI a command and getting a result; it's about building a dynamic, creative partnership.
We're moving far beyond basic text commands. The next frontier is multi-modal prompting, where we'll be able to mix and match different types of information—text, images, data, sound—to get far more sophisticated outputs from AI.
Think about what this makes possible. You could soon give an AI:
- An image of your new product and ask it to dream up an entire marketing campaign.
- A messy spreadsheet of sales numbers and tell it to write an engaging business report, complete with a narrative.
- An audio recording of a customer interview and have it instantly generate a deep sentiment analysis.
This isn't just about text anymore. It's about turning the AI into a true creative and analytical partner.
The Rise of the Prompt Engineer
This shift is creating a huge demand for people who are good at this. Companies are waking up to the fact that their expensive AI tools are only as good as the people operating them. It's not just hype; one AI safety company recently posted a job for a "Prompt Engineer and Librarian" with a salary between $250,000 and $335,000. That's a clear signal of how valuable this skill has become.
And this isn't just a fleeting trend. As AI gets woven into our daily work, knowing how to talk to these systems effectively will be a baseline requirement for staying relevant in almost every field, from graphic design to financial analysis.
Key Insight: At its core, prompt engineering isn't really a technical discipline. It's a new form of communication—the art of working with an intelligent system to bring an idea to life.
Ultimately, getting good at AI prompt engineering is about more than just boosting your productivity. It’s about learning to work alongside a powerful new form of intelligence. By mastering the art of asking the right questions, we don’t just get better answers from the AI. We become better thinkers and problem-solvers ourselves.
Got Questions About Prompt Engineering?
As you start working more with AI, you're bound to have questions. This whole field is moving at lightning speed, so it's completely normal to wonder what prompt engineering is all about, what it takes to be good at it, and where it's all headed. Let's tackle some of the most common questions head-on.
Think of this as a quick, no-fluff guide to help you get a solid handle on the discipline and what makes it tick.
What’s the Real Goal of AI Prompt Engineering?
At its core, AI prompt engineering is about getting an AI to give you exactly what you want. It's the art and science of writing instructions—or prompts—that are so clear and context-rich that a Large Language Model (LLM) can't help but produce an accurate, relevant, and high-quality response. The main goal is to eliminate confusion and maximize the AI's performance.
When you nail the prompt, you transform the AI from a somewhat unpredictable novelty into a powerful and reliable tool for just about any creative or analytical job.
Do I Need to Know How to Code to Be a Prompt Engineer?
Not necessarily. While coding skills are a huge plus for complex tasks like integrating an AI into software via an API, the heart of prompt engineering is really about communication, logic, and a bit of creativity. It's less about writing Python and more about thinking strategically.
The most crucial skills are ones many people already use every day:
- Sharp Writing: Can you get your point across clearly and concisely?
- Logical Thinking: Are you good at breaking down a big problem into small, manageable steps?
- Subject-Matter Expertise: Your knowledge in a specific field (like marketing or finance) is gold because it helps you give the AI the right context.
This opens the door for people from all sorts of backgrounds—writers, marketers, researchers, and teachers—to excel, using their natural language skills to get incredible results.
You can think of prompt engineering as the art of having a strategic conversation with a machine. You're using human language, but the level of precision needed is what makes it a true engineering skill.
What's Next for AI Prompt Engineering?
This field is going to look very different in a few years. It's already moving past just text. Soon, we'll be building multi-modal prompts, where you might feed an AI an image, a spreadsheet of data, and a voice command all at once to get a single, cohesive output.
We'll also see more "prompt-assistants"—specialized tools that help you build and refine your instructions on the fly. As the AI models themselves get smarter, the skill will evolve from just writing commands to something more like "AI coaching." You'll be guiding these incredibly intelligent systems through complex, multi-stage projects, acting more like a director than an operator.
Ready to stop guessing and start engineering your prompts? Join the community at Promptaa and get access to a library of expertly crafted prompts, powerful enhancement tools, and a network of creators. Sign up today and transform how you work with AI. Start creating better prompts now at Promptaa.